Bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder are different mental health conditions that are frequently confused. Because they share similar symptoms, it is not uncommon for people to wonder if there is a connection between them.
Navigating the world of mental health can feel like exploring an intricate maze. Two conditions that often lead to confusion and misperception are Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) and Bipolar Disorder. While both can present challenging symptoms, it’s crucial to understand that they are distinct disorders with their own unique characteristics.
In this article, we will delve into the maze of BPD and Bipolar, shedding light on their fundamental differences. From mood swings and emotional instability to impulsivity and social difficulties, we will explore how these conditions manifest and the impact they can have on individuals’ lives.
By understanding the nuances of BPD and Bipolar Disorder, we can foster empathy, reduce stigma, and cultivate a more informed perspective. Whether you are seeking personal insight into your own experiences or want to support a loved one, this article will equip you with the knowledge to differentiate between the two disorders, paving the way for accurate diagnoses and appropriate treatment plans.
Join us as we unravel the complexities and decode the differences between Borderline Personality Disorder and Bipolar Disorder.
Navigating mental health can feel daunting, but help is here!
What is Bipolar Disorder?
Bipolar disorder is a mental illness characterized by extreme shifts or alterations in mood. It is estimated that as many as 2.5 million Americans meet the diagnostic criteria for bipolar disorder, making it a prevalent mental illness in the United States. Bipolar disorder is typically diagnosed when one reaches their early twenties; however, diagnosis may occur during childhood or in the teen years, depending on symptoms. Currently, there is no cure for bipolar disorder, but mental health treatment can minimize the impact of symptoms.
When someone struggles with bipolar disorder, they experience three primary symptoms; mania, hypomania, and depression. Mania occurs when the person goes through a period of intense emotional highs. During mania or a “manic episode,” they will experience various emotions, including excitement, impulsivity, and euphoria. They will also have excessive amounts of energy, impacting their ability to sleep or rest.
Hypomania is a symptom commonly associated with bipolar II disorder. Hypomania is similar to mania; however, symptoms and emotional highs are not as notable or severe. Depressive episodes are the exact opposite of manic episodes. During an episode of depression, feelings of deep sadness, hopelessness, loss of energy, and lack of interest in commonly enjoyed activities occur.
What is Borderline Personality Disorder?
Borderline personality is described as a mental health condition that impacts how someone thinks and feels about themselves and others. Personality disorders like borderline personality disorder are characterized by patterns of thought, behavior, and feelings that are often unhealthy and inflexible. Someone with a borderline personality disorder will often struggle to foster healthy relationships with others.
They may also have difficulty managing everyday problems in ways others consider “acceptable.”
What is the Difference Between Borderline Personality Disorder vs. Bipolar Disorder?
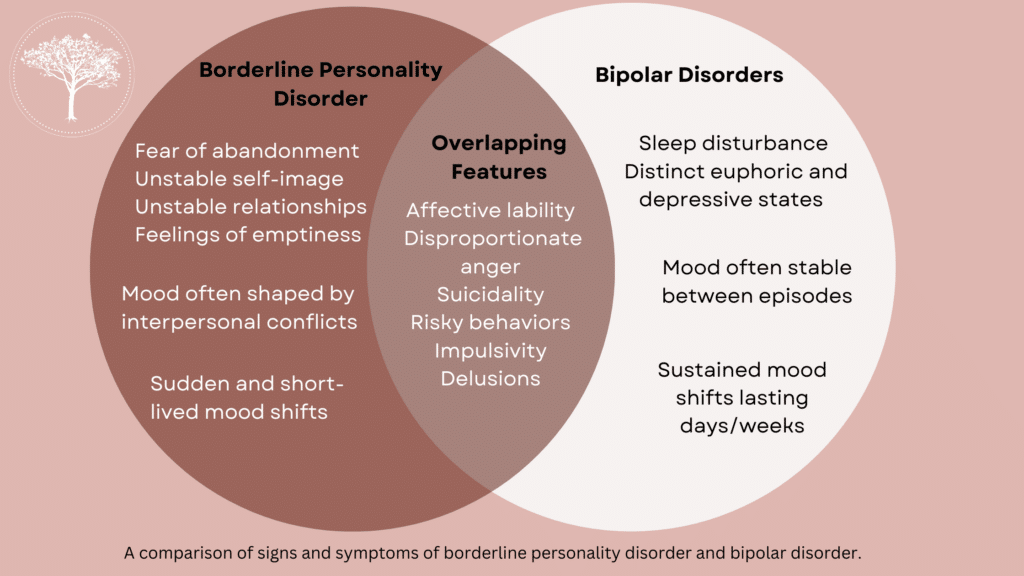
Bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder are often confused. Both conditions share many similar symptoms leading people to wonder if there is a connection between the two. To date, science has yet to confirm a link between the two illnesses, and they remain separate diagnoses in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Several characteristics separate these conditions.
Although mood changes characterize both, the quality of mood change may be different depending on the diagnosis. Someone who struggles with bipolar disorder will often experience mania and depression. In contrast, someone with a borderline personality disorder will experience intense and overwhelming feelings of loneliness, anger, hopelessness, and feelings of emotional pain.
The mood shifts associated with borderline personality disorder are usually short-lived and connected to environmental stressors such as disagreements with a loved one. Conversely, the mood shifts linked to bipolar disorder may last days or weeks and can occur without a known cause.
Symptoms and diagnostic criteria for BPD
To receive a diagnosis of Borderline Personality Disorder, individuals must meet specific criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). Some common symptoms of BPD include:
1. Frantic efforts to avoid real or imagined abandonment.
2. Unstable and intense relationships, alternating between idealizing and devaluing others.
3. Identity disturbance, marked by an unstable self-image or sense of self.
4. Impulsivity in potentially self-damaging areas, such as spending, sex, substance abuse, or reckless driving.
5. Recurrent suicidal behavior, gestures, or threats, or self-harming behaviors.
6. Intense and rapidly shifting emotions, often triggered by interpersonal conflicts or perceived abandonment.
7. Chronic feelings of emptiness or boredom.
8. Difficulty controlling anger and frequent displays of anger or aggression.
It’s important to note that individuals with BPD may not exhibit all of these symptoms, and the severity of symptoms can vary from person to person.
Symptoms and diagnostic criteria for BD
Bipolar Disorder is also diagnosed based on specific criteria outlined in the DSM-5. To receive a diagnosis of BD, individuals must have experienced at least one manic episode, which is characterized by:
1. A distinct period of abnormally elevated, expansive, or irritable mood lasting for at least one week.
2. Increased energy levels and a decreased need for sleep.
3. Grandiose beliefs or inflated self-esteem.
4. Racing thoughts or a rapid flow of ideas.
5. Increased talkativeness or pressured speech.
6. Impulsivity, such as engaging in risky behaviors or excessive spending.
In addition to manic episodes, individuals with BD may also experience depressive episodes, characterized by:
1. Persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or emptiness.
2. Loss of interest or pleasure in activities.
3. Significant weight loss or weight gain.
4. Insomnia or excessive sleep.
5. Fatigue or loss of energy.
6. Difficulty concentrating or making decisions.
7. Recurrent thoughts of death or suicide.
What Causes Bipolar and Borderline Personality Disorder?
There is no specific cause of borderline personality disorder. Like several similar mental health struggles, studies suggest the condition develops out of genetic factors, environmental factors, trauma, and parent/child connections during a child’s developmental stages.
Similarly, bipolar disorder does not have one specific cause. The development of bipolar disorder is linked to brain structure and functioning, family history of the illness, and genetic predisposition.
Overlapping symptoms and challenges in diagnosis
Given that both BPD and BD share some common symptoms, it can be challenging to differentiate between the two disorders. For example, impulsivity, mood swings, and difficulties in interpersonal relationships are present in both BPD and BD. However, the underlying causes and patterns of these symptoms differ significantly.
One of the primary challenges in diagnosis is that individuals with BPD often experience mood swings that resemble the intense highs and lows of BD. However, BPD mood swings are typically more reactive to immediate circumstances and are triggered by interpersonal conflicts or perceived abandonment. In contrast, BD mood swings are more prolonged and less reactive to immediate events.
It’s crucial for mental health professionals to conduct a thorough evaluation, considering the patterns and triggers of mood swings, the presence of other symptoms, and the individual’s personal history. Accurate diagnosis is essential for developing an appropriate treatment plan and ensuring individuals receive the support they need.
Your Path to Recovery Begins Here
Caring for someone with BPD or BD
Supporting a loved one with BPD or BD can be challenging, but it’s crucial to approach them with empathy, patience, and understanding. Here are some tips for caring for someone with BPD or BD:
1. Educate yourself: Learn about the disorder and its symptoms to better understand what your loved one is going through.
2. Communicate openly: Encourage open and honest communication, allowing your loved one to express their feelings without judgment.
3. Be patient and supportive: Recognize that your loved one may struggle with mood swings and emotional instability. Offer support and reassurance during difficult times.
4. Encourage treatment: Encourage your loved one to seek professional help and stay consistent with their treatment plan.
5. Take care of yourself: Caring for someone with BPD or BD can be emotionally draining. Make sure to prioritize your own well-being and seek support when needed.
How to Find Mental Health Treatment for Bipolar and Borderline Personality Disorder
Each disorder causes different symptoms, and therefore, the treatment methods for borderline personality disorder and bipolar disorder vary as well. It is important to find a treatment center where the treatment staff specializes in addressing the symptoms of your condition. It is also essential for your therapeutic team to understand the subtle yet significant differences between bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder.
Seeking help at a mental health rehab like Relevance Recovery can help you begin your journey toward putting your symptoms in the past. Although bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder are not necessarily “curable,” it is possible to learn safe and effective ways to manage symptoms, so these conditions are less impactful on your day-to-day health and happiness. Let the team at Relevance Recovery show you how as you connect with us to learn more about our programs that may support you along your journey.









