Understanding schizophrenia: What is it and How does it affect individuals?
Schizophrenia is a complex and often misunderstood mental disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by a range of symptoms including hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thoughts, and impaired cognitive abilities. Diagnosis of Schizophrenia and its symptoms can be extremely distressing and can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life and functioning.
It is important to understand that schizophrenia is not a split personality or a sign of weakness. It is a brain disorder that affects the way a person thinks, feels, and behaves. The exact cause of schizophrenia is still unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurodevelopmental factors.
Living with schizophrenia can be challenging, but it is important to remember that individuals diagnosed with this disorder can lead fulfilling and meaningful lives with the right support and treatment. By educating ourselves and others about schizophrenia, we can help reduce stigma and create a more inclusive society for everyone.
The Diagnosis Process: Signs and symptoms of schizophrenia
Receiving a diagnosis of schizophrenia can be overwhelming and confusing. It is essential to remember that a diagnosis is not a label or a definition of who you are, but rather a starting point for understanding and managing your symptoms.
Symptoms of Schizophrenia
According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), a diagnosis of schizophrenia requires at least two of the five main symptoms. These symptoms must have persisted for at least one month and significantly impact an individual’s ability to function in their work or relationships.
Delusions and Hallucinations
Delusions are false beliefs that a person holds steadfastly, even in the face of contradictory evidence. For example, a schizophrenic patient might believe that they are being followed or that they possess extraordinary abilities. Hallucinations, on the other hand, involve perceiving things that aren’t there. They can be visual, auditory, or involve any of the senses, but hearing voices is the most common hallucination in schizophrenia.
Disorganized Speech
Individuals with schizophrenia often exhibit disorganized speech. Their conversations may seem illogical, with their thoughts “derailing” from one topic to another. In some cases, their speech may be so muddled that it becomes impossible to understand.
Extremely Disordered Thinking and Behavior
The thinking of people with schizophrenia can be very disorganized, affecting all aspects of their behavior. They may exhibit unpredictable agitation, bizarre postures, or a lack of response (catatonia). Moreover, they may struggle with everyday tasks like personal hygiene.
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it is crucial to seek professional help. A diagnosis of schizophrenia is typically made by a mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist, who will conduct a thorough evaluation and consider the individual’s symptoms, medical history, and family history.
Evaluations for Schizophrenia
To get the diagnosis of schizophrenia, doctors rely on a combination of evaluations. These include interviews about the patient’s symptoms and psychiatric history, physical examinations to rule out medical causes, and psychological evaluations by a licensed mental health professional.
Physical Exam
The first step in the diagnostic process is usually a physical exam. This helps doctors rule out other issues that could be causing the symptoms. Certain neurological disorders, for example, epilepsy, brain tumors, encephalitis, and endocrine and metabolic problems, can sometimes mimic symptoms of schizophrenia. Infectious diseases and autoimmune conditions involving the central nervous system may also present similar symptoms. If necessary, doctors might order further tests, including brain imaging techniques such as CT scans or MRIs.
Tests and Screenings
While lab results and imaging studies are usually normal in people who have schizophrenia, they are essential for ruling out other conditions. Furthermore, certain behaviors related to mental disorders, such as excessive water drinking, might show up as metabolic problems in lab results. Toxicology screening can also be useful, as many substances, including alcohol, PCP, heroin, amphetamines, cocaine, and certain over-the-counter and prescription drugs can trigger psychotic symptoms.
Comprehensive psychiatric evaluation for schizophrenia
If the initial assessment suggests the possibility of schizophrenia, the next step is usually a comprehensive psychiatric evaluation. This evaluation is typically conducted by a psychiatrist or a psychologist who specializes in mental health disorders, including schizophrenia. The purpose of this evaluation is to gather more detailed information about the individual’s symptoms, experiences, and overall functioning.br/>
During the evaluation, the healthcare provider will conduct a thorough interview, asking in-depth questions about the individual’s symptoms, their duration, and their impact on daily life. They may also inquire about any past or current medical conditions, substance abuse history, and any medications the individual may be taking. This information helps the healthcare provider rule out other possible causes for the symptoms and ensures an accurate diagnosis.
The psychiatric evaluation may also involve the use of standardized assessment tools or scales to further evaluate the individual’s symptoms and level of functioning. These tools provide a standardized way of assessing and monitoring symptoms over time, allowing for more accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Dealing with the initial diagnosis: Emotions and reactions
Receiving a diagnosis of schizophrenia can evoke a wide range of emotions, including confusion, fear, sadness, and even relief. It is important to give yourself time to process these emotions and to seek support from loved ones or mental health professionals.
It is normal to have questions and concerns about the future. You may worry about how the diagnosis will impact your relationships, career, and overall quality of life. Remember that you are not alone. There are support networks and resources available to help you navigate this journey.
Opening up to family and friends about your diagnosis can be an important step in building a support system. While some people may struggle to understand or accept your diagnosis, others will be there to offer love, understanding, and encouragement. Connecting with support groups and online communities can also provide a sense of belonging and understanding.
Remember to be patient with yourself. It takes time to adjust to a new diagnosis and to find the right treatment and coping strategies that work for you. Reach out for professional help, consider therapy or counseling, and explore self-care practices that promote your overall well-being.
Diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia
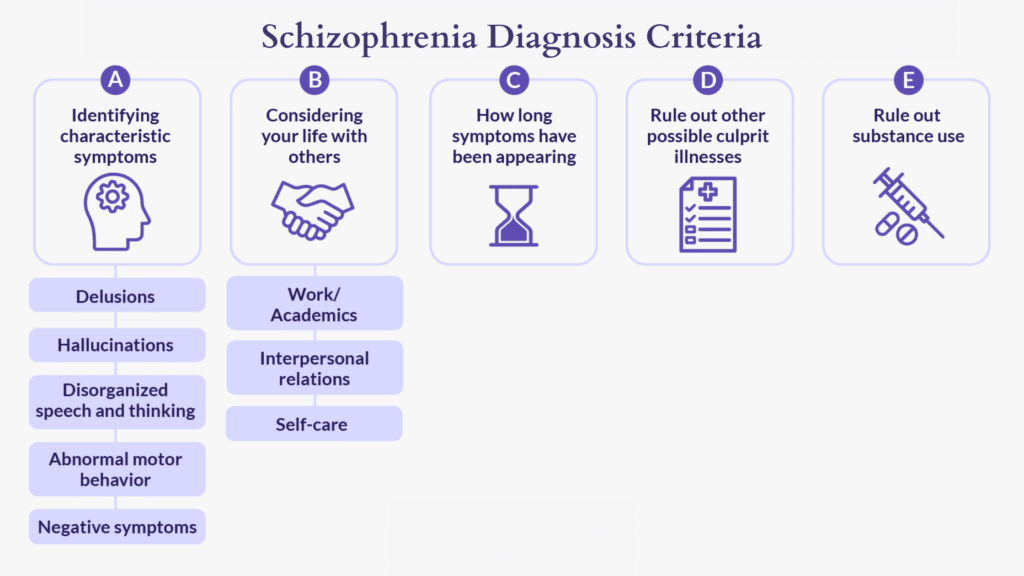
The diagnosis of schizophrenia is based on specific criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) published by the American Psychiatric Association. According to the DSM-5, to be diagnosed with schizophrenia, an individual must meet specific criteria related to the duration, severity, and impact of their symptoms.
The DSM-5 criteria for schizophrenia require the presence of at least two or more of the following symptoms for a significant portion of time during a one-month period: delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior, or negative symptoms. Additionally, the individual must experience a decline in functioning in at least one major area, such as work, interpersonal relationships, or self-care.
It is important to note that the diagnosis of schizophrenia is not made solely based on the presence of symptoms. The healthcare provider must also rule out other possible causes for the symptoms, such as substance abuse, medical conditions, or other mental health disorders. This process, known as a differential diagnosis, ensures that the diagnosis is accurate and that appropriate treatment can be provided.
Differential diagnosis: ruling out other conditions
As mentioned earlier, the diagnostic process for schizophrenia involves ruling out other possible causes for the individual’s symptoms. This is known as a differential diagnosis and is crucial in ensuring an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
The healthcare provider will carefully consider the individual’s medical history, family history, and the specific nature of their symptoms to determine if there are any other conditions that could better explain the experiences they are having. Substance abuse, certain medical conditions, and other mental health disorders can sometimes mimic the symptoms of schizophrenia, making a thorough evaluation essential.
To rule out other conditions, the healthcare provider may order additional tests, such as blood tests, imaging studies, or neurological assessments. These tests can help identify any underlying medical conditions or substance abuse that may be contributing to the individual’s symptoms. By ruling out other conditions, the healthcare provider can ensure that the diagnosis of schizophrenia is accurate and that appropriate treatment can be initiated.
Additional tests and assessments for schizophrenia
In addition to the initial assessment and comprehensive psychiatric evaluation, there may be additional tests and assessments conducted to further evaluate the individual’s symptoms and overall functioning. These additional tests can provide valuable information that can help guide treatment planning and monitor progress over time.
Neurocognitive testing is often used to assess the individual’s cognitive functioning, including attention, memory, problem-solving, and executive functioning. These tests can help identify specific areas of cognitive impairment and guide interventions to address these difficulties. Additionally, neuroimaging studies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be used to evaluate brain structure and function, providing further insights into the neurobiological basis of schizophrenia.
It is important to note that these additional tests and assessments are not always necessary for every individual seeking a diagnosis of schizophrenia. The decision to pursue further testing is made on a case-by-case basis, depending on the individual’s specific symptoms, history, and level of functioning.
Educating yourself about schizophrenia: Resources and Support Networks
Education is a powerful tool in managing and coping with schizophrenia. By learning about the disorder, its symptoms, and treatment options, you can become an active participant in your own care and make informed decisions.
There are numerous resources available to help you educate yourself about schizophrenia. Books, websites, and online forums provide valuable information and personal stories from individuals who have lived experience with the disorder. Additionally, mental health organizations and advocacy groups often offer educational materials, support groups, and helplines.
Take the time to research and find reliable sources of information. Look for reputable organizations and professionals who specialize in the treatment of schizophrenia. Engage in discussions and ask questions. The more you know, the better equipped you will be to advocate for yourself and make informed decisions about your treatment.
Remember that knowledge is power. By understanding schizophrenia and its effects, you can challenge misconceptions, break down stigma, and promote a more inclusive society.
Building a support system: Family, friends, and mental health professionals
Building a strong support system is essential for anyone living with schizophrenia. Having a network of understanding and supportive individuals can make a significant difference in the journey toward recovery and well-being.
Start by reaching out to trusted family members and friends. Share your diagnosis with them and let them know how they can support you. It is important to communicate openly and honestly about your symptoms, needs, and concerns. Encourage them to educate themselves about schizophrenia so that they can better understand your experiences.
In addition to your personal support network, it is crucial to work with mental health professionals who specialize in the treatment of schizophrenia. Psychiatrists, therapists, and counselors can provide you with the necessary guidance, therapy, and medication management to help you manage your symptoms and improve your overall quality of life.
Regular therapy sessions can provide a safe space to discuss your feelings, thoughts, and concerns. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other evidence-based therapies can help you develop coping strategies, manage stress, and improve your social and emotional functioning.
Remember that building a support system takes time and effort. Be patient with yourself and others, and don’t hesitate to reach out for help when you need it. Keep yourself patient after you receive the diagnosis of schizophrenia.
Treatment options for schizophrenia: Medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes
Managing schizophrenia can be done in a bunch of different ways, like taking meds, talking to a therapist, and making changes to your lifestyle. It’s important to work with your doctor to come up with a plan that fits your needs.
Antipsychotic Medications
- Risperidone – The antipsychotic drug risperidone is a popular choice for treating schizophrenia due to its ability to reduce both negative and positive symptoms. However, it is not without risks, as it may lead to weight gain and increased prolactin levels in some individuals.
- Olanzapine – Atypical antipsychotics, such as olanzapine, are prescribed for a variety of conditions. Olanzapine has been found to be particularly effective in reducing agitation and aggression in schizophrenia, however, it is important to note that it may also have adverse effects on the body, such as increased weight, decreased sedation, and alterations in metabolism.
- Quetiapine – Atypical antipsychotics, such as quetiapine, are commonly prescribed for their sedative properties. This medication has been found to be beneficial in the management of insomnia and anxiety in individuals with schizophrenia, however, it has been associated with drowsiness and increased body weight.
- Aripiprazole – The mechanism of action of aripiprazole as an antipsychotic drug is partially mediated by dopamine receptors. Aripiprazole has been found to be less prone to weight gain and metabolic adverse reactions than other antipsychotics, however, it has been associated with feelings of unease and agitation.
- Clozapine – The use of Clozapine is novel in the treatment of treatment-resistant schizophrenia. It is prescribed when other antipsychotic drugs have not been successful in treating the condition. Studies have demonstrated that Clozapine can reduce suicidal ideation and behavior in patients with schizophrenia. Nevertheless, it is necessary to monitor blood levels regularly due to the potential risks associated with the condition, such as granulocytopenia, which can be life-threatening.
Side effects and things to consider
Medication is an essential part of treating schizophrenia, however, there are other treatments available to assist individuals in developing coping strategies, improving social functioning, and increasing overall well-being. These treatments, which typically involve psychotherapy, CBT, and psychosocial intervention, are designed to address the specific challenges of schizophrenia, such as stress management, communication skills, and the promotion of independent living. These treatments are typically administered by qualified mental health professionals and can be customized to fit the individual’s individual needs and objectives.
Different Therapies for Schizophrenia
- Psychotherapy – Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is a range of treatments that focus on helping people recognize and address problematic feelings, ideas, and behavior. Most of the time, people in psychotherapy meet with a therapist either alone or with other people in a group.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) – CBT is a type of therapy that can help you learn how to manage stress and improve your social and emotional health. It can also help you feel more connected and understood in support groups and group therapy.
- Family Therapy – If you’re dealing with schizophrenia, family therapy is a key part of your treatment. It’s when you bring in family or close friends to come to therapy. The goal of family therapy is to help you communicate better, manage stress, and build support within your family.
Managing daily life with schizophrenia: Coping strategies and self-care tips
Living with schizophrenia requires ongoing self-care and the development of coping strategies that can help you manage your symptoms and maintain a fulfilling life.
Here are some tips for managing daily life with schizophrenia:
- Stick to a routine: Establishing a daily routine can provide structure and stability. Plan your activities, meals, and sleep schedule to maintain a sense of order and predictability.
- Practice stress management: Stress can exacerbate symptoms of schizophrenia. Explore stress management techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and mindfulness to help reduce stress and promote relaxation.
- Stay connected: Isolation can worsen symptoms of schizophrenia. Make an effort to stay connected with loved ones, engage in social activities, and join support groups or community organizations.
- Set realistic goals: Break down your goals into smaller, achievable steps. Celebrate your accomplishments and be kind to yourself if you experience setbacks.
- Take care of your physical health: Engage in regular exercise, eat a balanced diet, and prioritize sleep. Physical well-being is closely linked to mental health.
- Manage your medications: Take your medications as prescribed and communicate any concerns or side effects to your doctor. Develop a system to help you remember to take your medications regularly.
- Avoid drugs and alcohol: Substance abuse can worsen symptoms and interfere with treatment. Seek help if you are struggling with addiction.
Remember that everyone’s journey with schizophrenia is unique. It may take time to find the coping strategies and self-care practices that work best for you. Be patient, be kind to yourself, and seek support when needed.
Overcoming Stigma and Misconceptions: Advocacy and Raising Awareness
Unfortunately, stigma and misconceptions surrounding schizophrenia are still prevalent in society. This can lead to discrimination, social isolation, and a lack of understanding about the disorder.
Overcoming stigma starts with education and awareness. By sharing your story, challenging stereotypes, and advocating for yourself and others, you can help break down barriers and promote a more inclusive society.
Consider becoming an advocate for mental health and schizophrenia awareness. Participate in local events, share your experiences on social media, or volunteer with organizations that focus on mental health. By speaking out, you can help raise awareness, fight stigma, and create a more supportive environment for individuals living with schizophrenia.
Remember that your voice matters and your story has the power to inspire and educate others. Be brave, be proud of who you are, and know that you are not alone.
Finding hope and living a fulfilling life with schizophrenia
Receiving a diagnosis of schizophrenia can feel overwhelming, but it is important to remember that there is hope. With the right treatment, support, and self-care, individuals with schizophrenia can lead fulfilling and meaningful lives.
Finding hope starts with embracing your journey and seeking help when needed. Surround yourself with positive influences and individuals who believe in your potential. Participate in activities that bring you joy and a sense of purpose. Celebrate your achievements, no matter how small they may seem.
Remember that recovery looks different for everyone. It is not a linear process, and there may be ups and downs along the way. Be patient, be kind to yourself, and never give up.
Real Life Stories of people suffering from Schizophrenia
In order to gain a comprehensive comprehension of schizophrenia, it is essential to gain insight from the perspectives of individuals who are living with the condition. This article will provide insight into the resilience and recovery strategies employed by those who have managed to successfully cope with their mental health issues.
1. John’s Journey to Stability
“Being diagnosed with schizophrenia in my early twenties was a daunting journey. At first, acceptance was a struggle, and the symptoms felt overwhelming. Thanks to the unwavering support of my family and a comprehensive treatment plan involving therapy and medication, I reclaimed control over my life. Today, I proudly serve as a mental health advocate, leveraging my personal experiences to assist others on their path to recovery.” – John 👥🌟 #MentalHealth #Recovery #Advocate
2. Sara’s Path to Empowerment
“My journey with schizophrenia began in my teenage years. I faced numerous obstacles, including societal stigma and a lack of understanding from friends and family. Despite these challenges, I refused to let my diagnosis define me. Through therapy and support groups from Relevance Recovery, I learned coping mechanisms to manage my symptoms and developed a strong support network. Today, I am a successful artist and advocate for better mental health resources for individuals with schizophrenia.” – Sara 🌟
3. Mark’s Triumph over Adversity
“Life took a drastic turn for me when I got the diagnosis of schizophrenia in my thirties. Those initial days were tough, dealing with hallucinations and paranoia, and it became a challenge to maintain relationships and hold a job.
But I had an incredible treatment team by my side. Together, we found a medication regimen that worked for me. I also dove into cognitive-behavioral therapy, which helped me challenge and change those negative thought patterns.
Today, I’m proud to say that I’m happily married, I have a steady job, and I’m living a fulfilling life. It goes to show that with the right support and determination, we can overcome even the most challenging circumstances.” – Mark
Conclusion: Embracing your journey and seeking help when needed
Receiving a diagnosis of schizophrenia can be a life-altering experience, but it does not define you. It is important to remember that you are not alone on this journey. Reach out for support, educate yourself, and advocate for yourself and others.
By understanding schizophrenia, building a support system, exploring treatment options, and practicing self-care, you can manage your symptoms and live a fulfilling life.
Embrace your journey, seek help when needed, and never lose hope. You are strong, resilient, and capable of achieving great things.
CTA: If you or someone you know is struggling with suicidal thoughts, please reach out to a helpline or Relevance Recovery Treatment Center in New Jersey. Remember, you are never alone, and there is help available.









