Overcoming addiction is a challenging journey, but two powerful resources can provide support: Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) and 12-step Mutual Aid Groups. DBT combines cognitive-behavioral therapy with mindfulness to help manage emotions and change addictive behaviors. 12-step Groups like Alcoholics Anonymous offer a supportive community for sharing experiences and building a strong support system. Combining DBT and 12-step support enhances the chances of overcoming addiction and leading a fulfilling life.
Break Free from Addiction
Understanding Addiction And The Need for Effective Treatment
Addiction is a complex and chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by compulsive drug use despite harmful consequences. Addiction can take many forms, including substance abuse, alcoholism, gambling, and even addictive behaviors like compulsive eating or shopping. It not only affects the individual but also has a profound impact on their relationships, health, and overall well-being.
To effectively address addiction, it is crucial to understand its underlying causes. Addiction is often rooted in a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. Trauma, stress, and mental health disorders can also contribute to the development of addictive behaviors. Therefore, a holistic approach to treatment is essential for long-term recovery.
What is Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT)?
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) is a form of therapy that combines elements of cognitive-behavioral therapy with mindfulness practices. It was originally developed to treat individuals with borderline personality disorder, but its effectiveness in addressing addiction has been widely recognized.
DBT focuses on helping individuals develop skills to manage their emotions, improve their relationships, and cope with distressing situations. It emphasizes the concept of dialectics, which encourages individuals to find a balance between acceptance and change. By learning to accept themselves and their emotions while also working towards positive change, individuals can break free from destructive patterns of behavior.
The Principles and Techniques of DBT
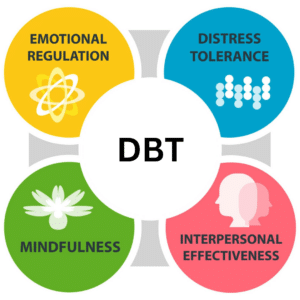
DBT is based on four key principles: mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotion regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness. These principles form the foundation of the therapy and guide individuals towards healthier coping mechanisms.
1. Mindfulness: Mindfulness is a central component of DBT. It involves being fully present in the moment, without judgment or attachment to thoughts or emotions. By practicing mindfulness, individuals can increase their self-awareness and develop a greater understanding of their triggers and cravings.
2. Distress tolerance: Addiction recovery is often accompanied by intense emotional distress. DBT helps individuals develop skills to tolerate distress without resorting to addictive behaviors. These skills include self-soothing techniques, distraction strategies, and radical acceptance of difficult emotions.
3. Emotion regulation: Many individuals turn to drugs or alcohol as a way to cope with overwhelming emotions. DBT teaches individuals how to identify and regulate their emotions in healthy ways. This includes learning to recognize emotional triggers, challenge negative thoughts, and develop effective coping strategies.
4. Interpersonal effectiveness: Healthy relationships and social support are crucial for recovery. DBT helps individuals improve their communication and relationship skills. It focuses on assertiveness, setting boundaries, and resolving conflicts constructively.
The Benefits of DBT in Addiction Recovery
DBT has been proven to be effective in treating substance abuse disorders. Numerous studies have shown that individuals who receive DBT in conjunction with other forms of treatment have better outcomes than those who receive traditional therapy alone.
The benefits of DBT in addiction recovery include:
1. Enhanced emotional regulation: DBT equips individuals with the skills to manage their emotions effectively. This reduces the likelihood of turning to drugs or alcohol as a way to cope with emotional distress.
2. Improved interpersonal relationships: Addiction often damages relationships, making it difficult to rebuild trust and establish healthy connections. DBT helps individuals develop healthy communication and relationship skills, which are essential for maintaining positive social support.
3. Reduced risk of relapse: DBT teaches individuals how to identify and challenge their addictive behaviors and thought patterns. By developing healthier coping mechanisms, individuals are better equipped to prevent relapse and sustain their recovery.
4. Increased self-acceptance and self-compassion: Addiction often leads to feelings of shame, guilt, and self-blame. DBT encourages individuals to practice self-acceptance and self-compassion, fostering a sense of worthiness and self-love.
By incorporating DBT into addiction treatment plans, individuals can gain the skills and tools necessary to overcome addiction and lead a healthier, more fulfilling life.
The History and Philosophy of 12-Step Programs
12-Step Mutual Aid Groups, such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) and Narcotics Anonymous (NA), have been instrumental in supporting individuals on their journey to recovery. These groups follow a set of guiding principles and offer a supportive community of individuals who have experienced similar struggles with addiction.
The 12-step philosophy was first introduced by Alcoholics Anonymous in the 1930s. It is based on the belief that addiction is a spiritual and progressive disease that requires ongoing support and self-reflection. The 12-step program provides a structured framework for individuals to work through the steps and principles necessary for recovery.
The 12-Step Program and Its Effectiveness in Addiction Recovery
The 12-step program consists of twelve steps that guide individuals toward recovery. These steps include admitting powerlessness over addiction, surrendering to a higher power, making amends, and helping others who are struggling with addiction.
The effectiveness of the 12-step program in addiction recovery has been widely studied and documented. Research has shown that individuals who actively participate in 12-step meetings and work through the steps are more likely to achieve and maintain sobriety.
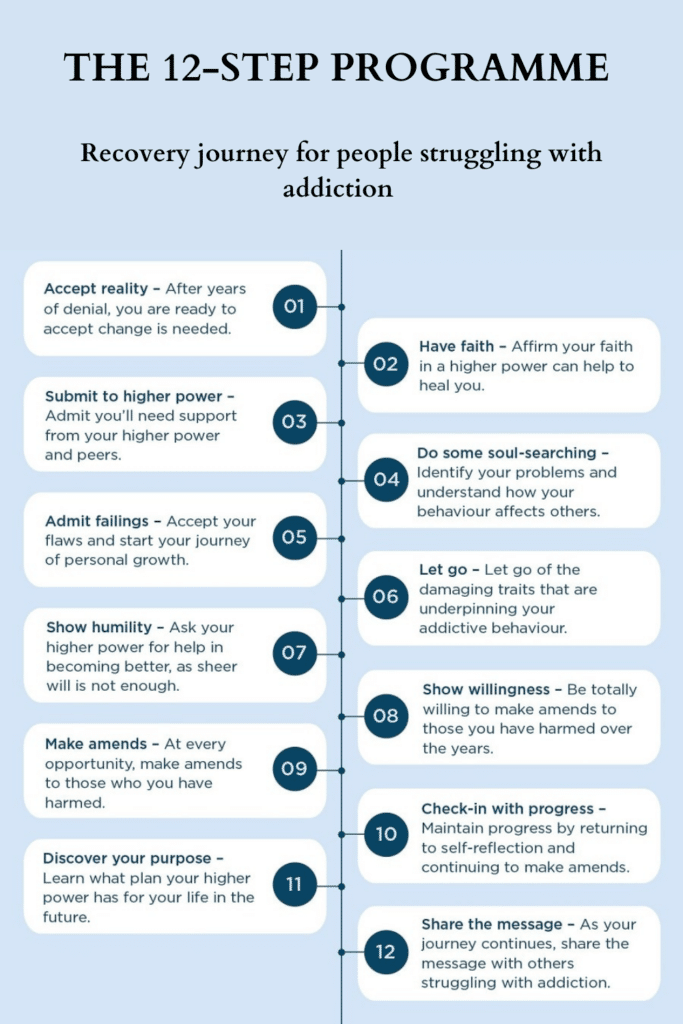
The benefits of 12-step programs in addiction recovery include:
1. Supportive community: 12-step Mutual Aid Groups provide a safe and non-judgmental space for individuals to share their experiences, struggles, and successes. The sense of belonging and support from others who have walked a similar path can be incredibly empowering.
2. Accountability: The 12-step program encourages individuals to take ownership of their recovery journey. By regularly attending meetings, sharing their progress, and working through the steps, individuals hold themselves accountable for their actions and commitment to sobriety.
3. Spiritual growth: The 12-step program emphasizes the importance of surrendering to a higher power. This can provide individuals with a sense of purpose, meaning, and spiritual growth, which can be instrumental in maintaining long-term recovery.
4. Continuous learning: 12-step programs offer a wealth of resources, literature, and tools for individuals to continue learning and growing in their recovery journey. This ongoing education helps individuals develop new coping strategies, expand their support networks, and stay motivated in their sobriety.
Your Path to Recovery Begins Here
Combining DBT and 12-Step Mutual Aid Groups for Holistic Treatment
While DBT and 12-step Mutual Aid Groups are powerful resources on their own, combining them can provide individuals with a comprehensive and holistic approach to addiction recovery.
DBT helps individuals develop the skills and tools necessary to manage their emotions, regulate their behaviors, and build healthier relationships. It provides a strong foundation for individuals to navigate the challenges of addiction recovery.
On the other hand, 12-step Mutual Aid Groups offer a supportive community of individuals who understand the struggles of addiction. They provide a safe space for sharing personal experiences, offering guidance, and building a strong support system.
Conclusion:
Overcoming addiction is a challenging journey, but with the right resources and support, individuals can achieve lasting recovery. Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) and 12-step Mutual Aid Groups offer unique and complementary approaches to addiction recovery.
DBT equips individuals with the skills to manage their emotions, regulate their behaviors, and build healthier relationships. It addresses the underlying causes of addiction and provides individuals with the tools necessary for long-term recovery.









