If your doctor has given you sedative-hypnotic medications, you might be curious about how long do barbiturates stay in your system. Barbiturates, which are central nervous system depressants, can linger in your system for different durations based on the type of drug test used.
Barbiturates typically remain detectable in blood for about 72 hours, in saliva for three days, and in urine for six weeks. They can also be detected in hair follicles for up to 3 months. These timelines vary depending on the barbiturate type, individual factors like metabolism and health, and the strength of the medication.
If you are taking barbiturates and have a detection test coming up, you might be wondering about how long do barbiturates stay in your system.
It’s important to understand the history of a drug to ensure its recovery and trust the process. Frank Salage, father of 2, overcome his battles with alcohol and drug abuse by trusting the process and getting adequate guidance from Relevance Recovery. You can know his story here.
This blog helps you understand the timelines of this drug in your system, its side effects, and drug tests to better understand barbiturates.
Wondering How to Detox !
What Are Barbiturates?
Barbiturates is a type of medication that helps people relax and fall asleep. They were widely used before, but nowadays, they are less commonly prescribed due to the risks associated with their use. Barbiturates can be habit-forming and cause heavy withdrawal symptoms.
Barbiturates were initially used to treat anxiety and insomnia, but safer medications like benzodiazepines have largely replaced them. However, they are still used in some cases, such as epilepsy, anaesthesia, and to help manage withdrawal symptoms from other medications.
Barbiturates Facts & Regulations
Barbiturates were once widely used to treat anxiety, insomnia, and other conditions. However, their use declined significantly in the 1970s due to concerns about physical dependence and behavioral changes. Despite this, they are still prescribed in certain situations, such as for seizure disorders, migraines, and sedation before procedures.
Barbiturates are controlled substances in the United States, with different classifications based on their potential for abuse and addiction. Schedule IV drugs, like phenobarbital, have a lower abuse potential, while Schedule II drugs, like amobarbital and pentobarbital, have a higher potential for misuse.
When Do Barbiturates Side Effects Kick-In?
Taking barbiturates reduces activity in the central nervous system (CNS) by increasing levels of GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). This results in a range of depressant effects, including:
- Euphoria
- Relaxation
- Sedation
- Drowsiness
- Sleepiness
- Confusion
- Impaired Judgment
- Reduced Inhibition
- Slurred Speech
- Poor Coordination
The effects of barbiturates typically begin within 30 minutes of ingestion and can last anywhere from 4 to 16 hours, depending on the type of barbiturate used. For instance:
- Ultra-short-acting barbiturates, such as thiopentone and methohexitone, have a shorter duration of action, lasting around 30 minutes.
- Short-acting barbiturates, like hexobarbitone, cyclobarbitone, pentobarbitone, and secobarbitone, can last for 2 hours.
- Intermediate-acting barbiturates, such as amobarbital, pentobarbital, and secobarbital, can have effects that last for 5 to 6 hours.
- Long-acting barbiturates, like phenobarbital, can have effects that persist for 12 to 24 hours.
These variations in duration are crucial to understand when considering the use of barbiturates or their effects on the body. Let’s explore how long do barbiturates stay in your system.
How Long Do Barbiturates Stay In Your System?
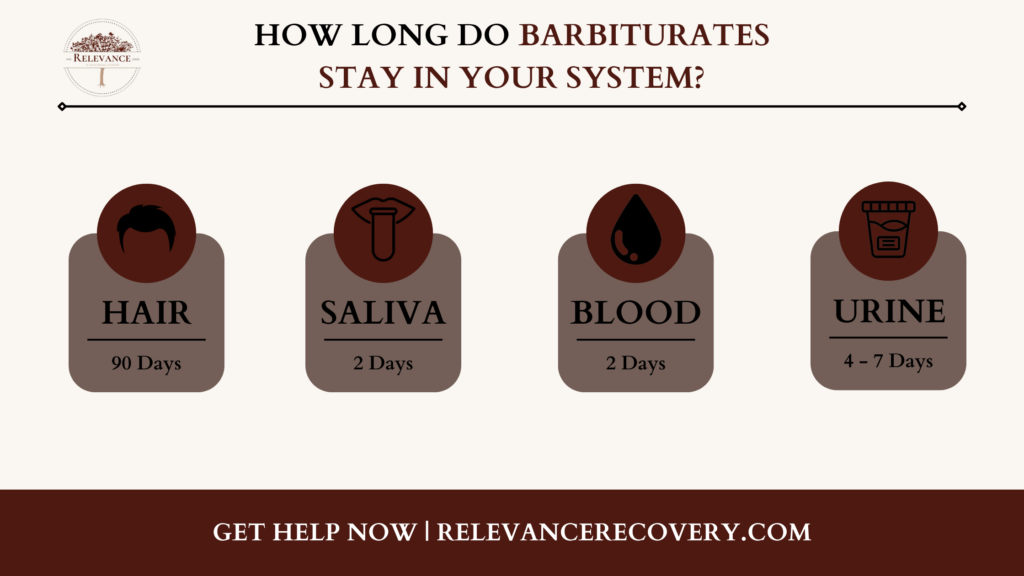
Even after the drug’s effects have worn off, there may still be traces of it left in your system.
Several factors influence how long do barbiturates stay in your system & remain detectable in your body:
● Body Mass
People with higher body mass often take larger doses, which can take longer to metabolize and clear out. This leads to longer detection times.
● Metabolism
Everyone has a unique metabolic rate, regardless of body size. If you have a slower metabolism, barbiturates will stay longer than if you have a faster metabolism.
● Health
Conditions like kidney or liver problems, blood circulation disorders, and other issues that affect how your body processes drugs can extend the timeline.
● Other Substances
Certain medications can either slow down or speed up how your body breaks down barbiturates. Even eating food before taking the drug can slow down the process.
● Dosage Habit
Higher doses and more frequent use require more time for your body to eliminate the drug. Long-term abuse can lead to very long detection windows.
So remember that your barbiturate clearance time may not match typical estimates. It depends on your unique physiology and drug use patterns. The only way to know for sure is to get tested.
Where Do Barbiturates Stay In Your System?
If you have been prescribed barbiturates and need to undergo a toxicology screen, here are the detection windows for barbiturates in your system:
● Blood test
Barbiturates can be detected in blood for up to 72 hours.
● Saliva test
They can be detected in saliva for up to 3 days.
● Urine test
They can be detected in urine for up to 6 weeks.
● Hair follicle test
They can be detected in hair follicles for up to 3 months.
These detection windows vary depending on the type of barbiturate, your health, and other factors.
Do Barbiturates Show Up On A Drug Test?
The 10-panel Drug Test includes an indicator for barbiturates. If you are taking this test, barbiturates will likely be detected in your system if you have recently used the drug.
Additionally, specific drug detection tests can be ordered to look for barbiturates. Authorities or formal organizations often request these tests for various purposes, mainly if there is a history of barbiturate use.
Your Path to Recovery Begins Here
FAQs
Que: How long do you test positive for barbiturates?
Ans: The urine barbiturate screening test detects secobarbital at a concentration of 200 ng/mL or greater, and barbiturates may be detected in urine 1-21 days after ingestion.
Que: How long are barbiturates detectable in blood?
Ans: Barbiturates: 2-4 days in urine and 1-2 days in blood. Benzodiazepines: 3-6 weeks in urine and 2-3 days in blood.
Que: What drug shows up as barbiturates?
Ans: Secobarbital (Seconal) is the barbiturate in urine tests at a concentration of 200 ng/mL or more significant.
Que: How are barbiturates eliminated?
Ans: Barbiturates are eliminated through hemodialysis and hemoperfusion, which enhance their removal from the body. The efficacy of these methods is particularly well-established for phenobarbital.
Que: What color indicates a positive test for barbiturates using the modified Dille-Koppanyi test?
Ans: In the modified Dille-Koppanyi test, the sample is dissolved in 1 ml of ethanol on a test plate, followed by adding one drop of solution and agitation. A blue-violet color indicates the presence of barbiturates.
Conclusion
Barbiturates are medications that help you relax or feel drowsy. They’ve been around since the 1860s and are still used for various conditions today. Although they’re not as common anymore, these drugs still benefit many people with a range of medical issues.
However, it’s essential to use barbiturates cautiously and precisely as prescribed. Your healthcare provider can give you more information on what to expect and how to use these medications effectively. If you’re still wondering, “How long do barbiturates stay in your system?” your healthcare provider can guide you.









