Do you find yourself constantly overwhelmed, restless, or apprehensive, with anxiety affecting your daily life and relationships? If so, it’s time to consider seeking a professional anxiety diagnosis, which is the first step toward finding the right treatment and support.
When it comes to diagnosing anxiety, consulting with a qualified healthcare professional is essential. They will conduct a comprehensive evaluation, which may include a detailed assessment of your symptoms, medical history, and any underlying conditions.
Anxiety can manifest in various forms, such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, or social anxiety disorder. However, an accurate diagnosis is the key to determining the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. Understanding the diagnostic process empowers you to ask the right questions, collaborate with your healthcare provider, and make informed decisions about your mental health.
From comprehending the criteria for diagnosing anxiety disorders to exploring the various assessment tools used, this blog will equip you with the knowledge you need to take control of your anxiety journey. So, let’s dive in and unravel the complexities of the diagnostic process to pave the way for an accurate anxiety diagnosis and effective treatment.
Are You Ready to Reclaim Your Life from Personality Disorders?
Importance of an Accurate Anxiety Diagnosis
Anxiety disorders, among the most common mental health challenges, affect millions of individuals worldwide. While it’s normal to experience occasional anxiety, chronic or severe anxiety can be debilitating. This is where the importance of an accurate anxiety diagnosis becomes evident. Let’s understand why precision in diagnosis matters, how it impacts individuals, and why it is essential for society as a whole.
I. The Personal Impact of Anxiety
– Personal Well-Being
Anxiety can erode an individual’s overall well-being. Symptoms such as persistent worry, restlessness, irritability, sleep disturbances, muscle tension, and even physical health problems can make life challenging. An accurate diagnosis is the cornerstone for understanding the specific anxiety type and tailoring the treatment accordingly.
– Effective Treatment
An accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Various anxiety disorders respond differently to therapeutic approaches. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), medication, or a combination of both may be recommended based on the diagnosis. This personalized approach increases the chances of successful outcomes.
– Reducing Stigma
An accurate diagnosis also plays a pivotal role in diminishing the stigma surrounding mental health. When individuals comprehend their condition and its origins, they can better communicate their needs to friends, family, and employers, thus contributing to a more supportive environment.
II. Societal Impact
– Economic Costs
Untreated or inaccurately diagnosed anxiety carries significant economic costs. Individuals struggling with anxiety disorders may face employment difficulties due to their symptoms, leading to decreased productivity and increased healthcare expenses. Accurate diagnoses can help alleviate these financial burdens on both individuals and society.
– Healthcare System Efficiency
Anxiety-related issues often result in overutilization of healthcare resources, including emergency room visits and doctor’s appointments. With precise diagnoses, healthcare providers can allocate resources more efficiently, ensuring that patients receive the most appropriate care promptly.
Why Seek Professional Diagnosis?
Before we dive into the steps, it’s crucial to understand why professional diagnosis is essential:
- Accurate Assessment: A professional assessment ensures that your symptoms are accurately diagnosed. This is crucial because anxiety disorders can manifest differently in various individuals.
- Effective Treatment: A proper diagnosis enables healthcare providers to recommend the most effective treatments, such as therapy, medication, or a combination of both.
- Validation: A professional diagnosis can validate your experience and help reduce the stigma associated with mental health issues.
- Access to Support: A diagnosis opens doors to support networks, counseling, and resources designed to help individuals manage their anxiety.
Step 1: Recognizing the Signs of Anxiety
The journey toward professional diagnosis begins with recognizing the signs and symptoms of anxiety. Anxiety can manifest in various ways, such as excessive worry, restlessness, muscle tension, and difficulty concentrating. If these symptoms persist and significantly impact one’s daily life, it’s important to acknowledge the need for professional assistance.
Step 2: Consultation with a Primary Care Physician
The first step in seeking a professional diagnosis is often scheduling an appointment with a primary care physician (PCP). Whether you are an adult or a teenager, your PCP can conduct an initial assessment to discuss your anxiety symptoms. During this visit, the PCP will perform a physical examination and inquire about the duration and severity of the symptoms.
Step 3: Referral to a Mental Health Specialist
After the initial evaluation, the PCP may refer you to a mental health specialist, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist. Mental health specialists are trained to diagnose and treat various anxiety disorders.
Step 4: Comprehensive Diagnostic Assessment
The mental health specialist will conduct a comprehensive diagnostic assessment, which typically includes:
- Thorough interviews to gather detailed information about your mental health history, the nature of your symptoms, and the impact of anxiety on your daily life.
- Administration of standardized questionnaires and assessment tools specifically designed to measure anxiety levels and identify the type of anxiety disorder, if present.
- Collaboration with family members, especially teenagers, to gather additional information and provide a comprehensive evaluation.
Step 5: Receiving a Formal Diagnosis
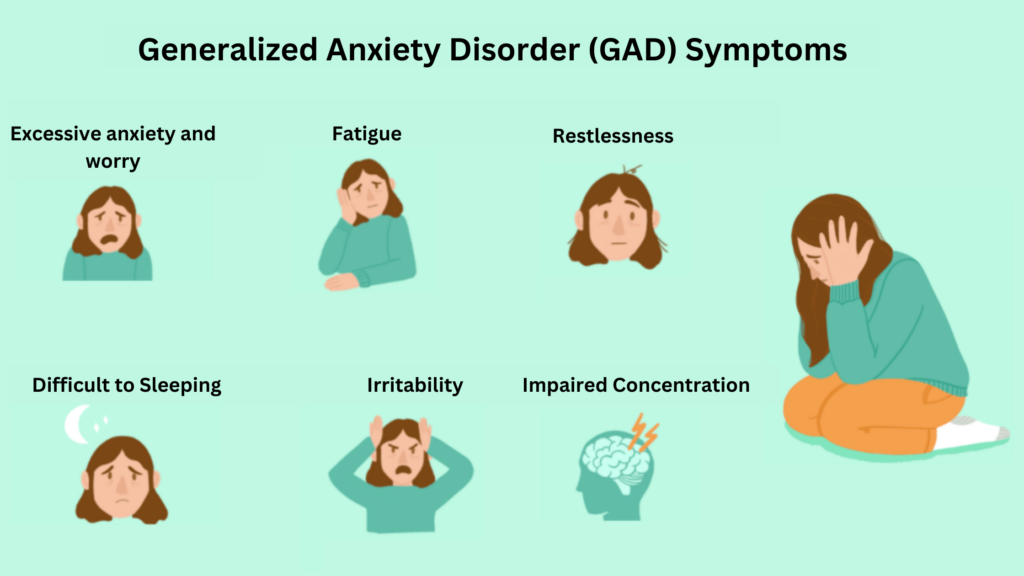
Upon completing the evaluation, the mental health specialist will provide a formal diagnosis. This diagnosis will specify the type of anxiety disorder you may have, such as Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), Social Anxiety Disorder, or Panic Disorder, if applicable.
Step 6: Creating a Personalized Treatment Plan
Following a formal diagnosis, the mental health specialist will work with you to create a personalized treatment plan. Treatment for anxiety can encompass various approaches, including:
Psychotherapy (talk therapy)
Medication, when deemed necessary
Anxiety management techniques
Lifestyle modifications
Support from family and peers
Types of Diagnostic Tests and Assessments for Anxiety
The various diagnostic tests and assessments used by healthcare professionals to identify and understand different anxiety disorders are:
I. Clinical Interviews
– Structured Clinical Interviews: Mental health professionals often use structured interviews with standardized questions to assess anxiety disorders. The Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI) and the Anxiety and Related Disorders Interview Schedule for DSM-5 (ADIS-5) are examples of these structured interviews.
– Unstructured Interviews: In unstructured interviews, clinicians engage in open-ended discussions with patients to gather information about their symptoms, history, and emotional experiences. This approach allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the individual’s condition.
II. Self-Report Questionnaires
– Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7 (GAD-7): This widely used questionnaire assesses generalized anxiety disorder by asking patients to rate the frequency of seven anxiety-related symptoms over the past two weeks.
– Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9): While primarily used to diagnose depression, the PHQ-9 also screens for anxiety symptoms. It consists of nine questions that assess various emotional states.
– Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI): The BAI is a self-report questionnaire with 21 multiple-choice questions that assess the severity of common anxiety symptoms.
III. Psychological Assessments
– Beck Depression Inventory (BDI): Although designed to measure depression, the BDI can also be useful in assessing anxiety symptoms. It consists of 21 multiple-choice questions.
– Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A): This clinician-administered scale evaluates the severity of anxiety symptoms by assessing factors such as mood, tension, and physical symptoms.
IV. Physical Examinations
– Blood Tests: In some cases, a healthcare provider may order blood tests to rule out underlying medical conditions that could be contributing to anxiety symptoms, such as thyroid problems or vitamin deficiencies.
– Neuroimaging: Although not a routine diagnostic test, neuroimaging techniques like functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) can help researchers better understand the neural pathways associated with anxiety disorders.
V. Observation and Behavioral Assessments
– Behavioral Observations: Mental health professionals may observe and document an individual’s behavior, looking for signs of anxiety, such as restlessness, avoidance, or repetitive behaviors.
– Situational Assessments: Behavioral assessments can also involve placing the individual in anxiety-inducing situations to observe their reactions and responses.
VI. Psychological Testing
– Personality Tests: Psychological tests, such as the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI) or the Rorschach test, may provide insights into an individual’s psychological makeup and potential anxiety symptoms.
– Cognitive Tests: Tests assessing cognitive functioning can help determine if cognitive factors are contributing to anxiety, such as worry or rumination.
Your Path to Recovery Begins Here
Challenges in Diagnosing Anxiety Disorders
While diagnosing anxiety disorders is essential for effective treatment, the process is not without its challenges. Here are some of the complexities and obstacles that mental health professionals and individuals may encounter when diagnosing anxiety disorders.
I. Overlapping Symptoms
One of the primary challenges in diagnosing anxiety disorders is the overlap of symptoms with other mental health conditions. Conditions such as depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) can share symptoms with anxiety disorders. This overlap can make it difficult to pinpoint the exact condition, leading to potential misdiagnosis.
II. Variability in Symptom Presentation
Anxiety disorders do not present in a one-size-fits-all manner. Symptoms can vary significantly from one individual to another. Some may experience predominantly physical symptoms like racing heart or digestive issues, while others may primarily exhibit cognitive symptoms such as excessive worry and rumination. This variability in symptom presentation can complicate the diagnostic process.
III. Co-Occurring Conditions
Many individuals with anxiety disorders also experience co-occurring mental health conditions, such as substance use disorders or other mood disorders. The presence of these co-occurring conditions can make it challenging to disentangle the specific anxiety disorder’s symptoms.
IV. Stigma and Self-Denial
The stigma around mental health issues can lead individuals to deny or downplay their symptoms. Fear of judgment or concerns about being labeled can deter people from seeking a diagnosis, further complicating the process.
V. Lack of Awareness
Both individuals and healthcare providers may not be fully aware of the range of anxiety disorders and their symptoms. This lack of awareness can result in underdiagnosis or misdiagnosis.
VI. Cultural Factors
Cultural factors can influence the expression of anxiety symptoms and individuals’ willingness to seek help. Different cultural norms and values can impact the recognition and reporting of anxiety-related concerns.
VII. Comorbidity
Comorbidity refers to the presence of multiple psychiatric conditions simultaneously. Many individuals with anxiety disorders also experience other mental health conditions, which can complicate the diagnostic process. Accurately identifying and addressing all co-occurring conditions is essential for effective treatment.
The Bottom Line
Seeking a professional diagnosis for anxiety is the vital inaugural stride in addressing this prevalent mental health concern. It opens the door to precise assessment, personalized treatment, and access to the support and resources essential for an enhanced quality of life. Although the diagnostic path may present its share of complexities and hurdles, comprehending its importance empowers individuals to seize control of their mental well-being. If you identify anxiety symptoms in yourself or someone you know, do not hesitate to reach out for professional assistance. Remember that help is readily available, marking the initial stride toward a brighter, anxiety-free future.









