Like many chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease, addiction can be treated, but it cannot be cured. For this reason, addiction is a struggle that many will face for the rest of their lives to varying degrees. While some people may complete an addiction treatment program and remain sober throughout their lives, others will experience one or more relapses as they navigate the challenges that accompany lasting sobriety. Drug or alcohol use disorders are considered chronic relapsing conditions because many people will inevitably relapse at some point. There are many contributing factors to relapse, including the severity of addiction and the substance used.
Relapse isn’t the end; it’s a chance to get back on track!
What is a Drug Relapse?
When someone is addicted to drugs or alcohol, they struggle with a range of physical, psychological, and behavioral symptoms that are complex and difficult to change. Substance use leads to physical and psychological changes to the brain and many vital body systems. Depending on one’s unique relationship with substances, these changes may be difficult to manage or reverse. The deeply rooted nature of addiction is what often leads to relapse.
When someone experiences a relapse, they return to using their substance of choice after a period of sobriety. Although relapse is understood to be a moment in time, it is essential to know that relapse is not sudden. The end result of a slow return to the harmful behaviors drove the urge to use. It is also essential to be aware of the signs of relapse in a friend or loved one. Knowing what the signs of a potential relapse look like can help ensure you or a loved one gets the help they need early. Early and proactive treatment can help prevent overdose or a drug-related medical emergency.
A final yet vital fact to mention about relapse is that it is not uncommon, nor does it indicate addiction treatment “failed.” The data about relapse statistics have not improved over the last few years. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration states that the relapse rate for all substances is between 40 and 60%.
Understanding relapse: What is it and why does it happen?
Relapse is defined as the recurrence of substance abuse after a period of abstinence. It is important to understand that relapse is not a sign of weakness or lack of willpower. Addiction is a complex disease that affects the brain, and relapse can be a natural part of the recovery process for many individuals.
One of the primary reasons for relapse is the brain’s response to the absence of the substance. When someone stops using drugs or alcohol, their brain has to adjust to the new normal. During this adjustment period, the brain may experience cravings and withdrawal symptoms, making it challenging to maintain sobriety. Additionally, external factors such as stress, social pressure, and environmental triggers can also contribute to relapse.
It’s crucial to approach relapse with compassion and understanding. Relapse is an opportunity for growth and learning, and it’s important to remember that recovery is a lifelong journey. By understanding the underlying causes of relapse, individuals can develop strategies to prevent and manage relapse effectively.
Signs and triggers of relapse
Recognizing the signs and triggers of relapse is an essential step in preventing its occurrence. There are several warning signs to watch out for, including:
1. Emotional instability: Mood swings, irritability, and feelings of restlessness can indicate an impending relapse.
2. Social withdrawal: Isolation and distancing oneself from support networks can be a sign of potential relapse.
3. Neglecting self-care: A decline in personal hygiene, disinterest in hobbies, and neglecting responsibilities may indicate a relapse.
4. Increased secrecy: Lying, hiding substance use, and being evasive about one’s whereabouts can be signs of relapse.
5. Cravings: Intense cravings for drugs or alcohol can be a powerful trigger for relapse.
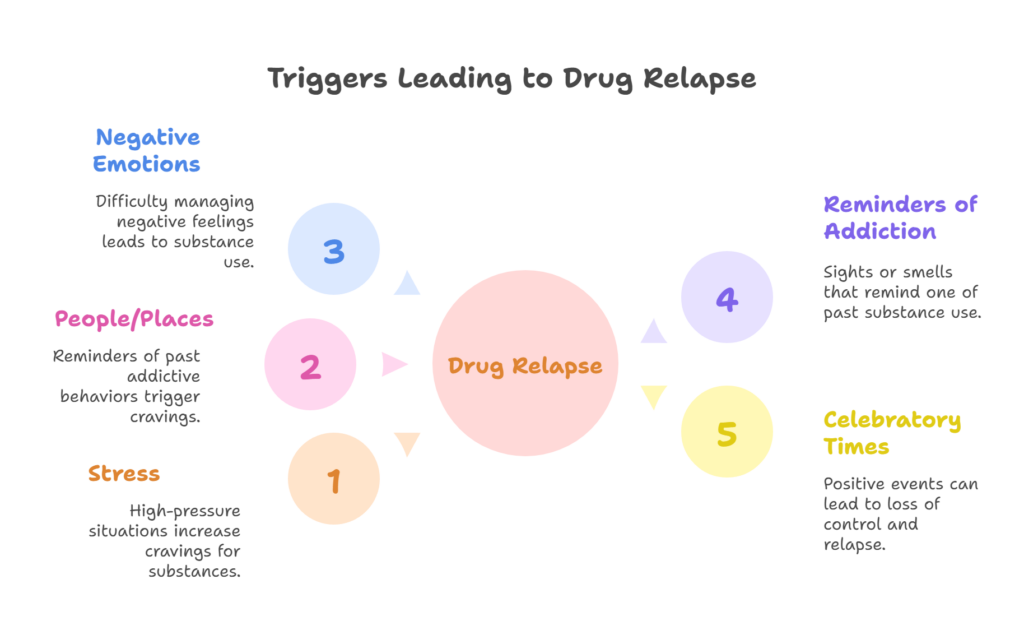
Triggers are situations, people, or emotions that can lead to cravings and ultimately result in relapse. Common triggers include stress, negative emotions, exposure to substances, social situations involving substance use, and even positive emotions such as celebration or excitement. Identifying personal triggers is crucial for developing an effective relapse prevention plan.
The importance of a relapse prevention plan
A relapse prevention plan is a personalized strategy that individuals can develop to anticipate and manage potential relapse triggers. It serves as a roadmap to navigate the challenges of recovery and helps individuals stay on track toward their sobriety goals. A relapse prevention plan typically includes the following components:
1. Identifying triggers: By recognizing personal triggers, individuals can develop strategies to avoid or manage them effectively.
2. Creating a support network: Building a strong support system is crucial for maintaining recovery. This can include family, friends, support groups, or a sponsor.
3. Implementing coping mechanisms: Developing healthy coping mechanisms is essential for managing cravings and stressful situations. This can include activities such as exercise, meditation, journaling, or engaging in hobbies.
4. Setting boundaries: Establishing boundaries with people or situations that may jeopardize recovery is an important aspect of relapse prevention.
5. Regular self-reflection: Engaging in regular self-reflection can help individuals identify patterns, strengths, and areas for growth in their recovery journey.
By having a relapse prevention plan in place, individuals can feel empowered and equipped to handle potential setbacks. This plan serves as a reminder of their commitment to sobriety and provides a roadmap for navigating the challenges of recovery.
What Drug Has the Highest Relapse Rate?
Although relapse rates for opioid drugs and other substances are indeed high, heroin (also an opioid) has the highest rate of relapse of any drug. Statistics for heroin addiction relapse are as high as 90%, according to a range of studies. Some studies suggest relapse rates for heroin addiction are even higher than 90%. Perhaps even worse is the fact that of the more than 90% of patients who experience relapse, as many as 59% relapse within one week of leaving their addiction treatment program.
Coping strategies for dealing with cravings
Cravings are a common challenge faced by individuals in recovery, and having effective coping strategies is crucial for managing them. Here are some strategies that can help individuals navigate cravings:
1. Mindfulness and meditation: Practicing mindfulness and meditation techniques can help individuals observe their cravings without judgment and allow them to pass without acting on them.
2. Distract and redirect: Engaging in activities that divert attention away from cravings, such as exercise, reading, or spending time with loved ones, can be effective in managing cravings.
3. Healthy coping mechanisms: Developing healthy coping mechanisms, such as deep breathing exercises, journaling, or engaging in creative outlets, can provide an alternative outlet for managing cravings.
4. Seeking support: Reaching out to a trusted friend, sponsor, or support group during moments of intense cravings can provide the necessary support and encouragement to stay on track.
By implementing these coping strategies, individuals can regain control over their cravings and reduce the risk of relapse.
Learning from setbacks: Turning relapse into a learning opportunity
Relapse can be a powerful learning opportunity. It allows individuals to gain insight into their triggers, vulnerabilities, and areas for growth. Rather than viewing relapse as a failure, reframing it as a learning experience can be empowering. Here are some steps to turn relapse into a learning opportunity:
1. Reflect on the relapse: Take time to reflect on the circumstances leading up to the relapse. Identify the triggers, emotions, and situations that contributed to the relapse.
2. Seek support: Reach out to a support system, therapist, or counselor to discuss the relapse and gain insights and guidance.
3. Adjust the relapse prevention plan: Use the relapse as an opportunity to reassess and refine the relapse prevention plan. Identify areas that need strengthening and develop strategies to avoid future relapses.
4. Practice self-compassion: Be kind and understanding with oneself. Recognize that setbacks are a natural part of the recovery process and that learning from them is an essential aspect of growth.
By approaching relapse as a learning opportunity, individuals can gain valuable insights, strengthen their recovery strategies, and increase their chances of long-term success.
Your Path to Recovery Begins Here
Building resilience and self-compassion
Building resilience and cultivating self-compassion are essential for individuals navigating the road to recovery. Recovery is a journey filled with ups and downs, and setbacks are a natural part of the process. Here are some strategies to foster resilience and self-compassion:
1. Practice self-care: Engaging in activities that promote self-care, such as practicing mindfulness, engaging in hobbies, or taking time for oneself, can enhance overall well-being and resilience.
2. Celebrate progress: Acknowledging and celebrating milestones, no matter how small, can boost self-confidence and motivation.
3. Learn from setbacks: Rather than viewing setbacks as failures, approach them as learning opportunities. Reflect on what triggered the relapse and identify strategies to prevent similar situations in the future.
4. Practice self-compassion: Treat oneself with kindness and understanding. Recognize that recovery is a challenging process, and it’s important to be patient and forgiving with oneself.
By building resilience and cultivating self-compassion, individuals can navigate setbacks with grace and continue moving forward on their journey to lasting recovery
Conclusion
If you or a loved one experiences relapse after treatment for heroin addiction (or any other addiction), it is vital to seek help when you notice any warning signs of relapse. Early help and detox support are crucial to helping your loved one manage relapse as safely as possible. When someone relapses on heroin, they are in danger of significant complications, including overdose and potentially life-threatening medical consequences. Getting back to rehab and seeking help to get back on track with your sobriety are vital steps towards resuming your recovery journey.
At a rehab like Relevance Recovery, members of our treatment team will work with you on a treatment plan that will help you get sober again while reinforcing relapse prevention skills that can help prevent further relapse in the future. Overcoming heroin addiction is hard. The impacts that heroin use has on the body and mind take time to heal. If you have experienced relapse or are worried a friend or loved one has, contact Relevance Recovery for help today.









