Many individuals face the painful reality where substance use and mental health issues intertwine, making the path to healing seem impossible without the proper co-occurring disorders treatment. Addiction doesn’t happen alone. It is often linked to mental health disorders. These disorders can worsen addiction symptoms. When addiction and a mental health disorder occur together, it’s called a co-occurring disorder. Treating both is essential for recovery.
Co-occurring disorders are a genuine health concern in the United States. In a conversation with Michael Alago, he highlighted his struggles with addiction and the trauma of drug withdrawal. From growing up in Brooklyn and finding success in music with Metallica and Cindy Lauper, he faced tough times with addiction. Alago shares how therapies and treatments helped him through the highs and lows of recovery.
To know about co-occurring disorders in-depth, read this article, which highlights co-occurring disorders, covering the symptoms, causes, and co-occurring disorders treatment options.
Struggling with addiction and mental health?
What are Co-Occurring Disorders?
Co-occurring disorders occur when someone experiences both a mental health condition and substance abuse at the same time. For example, a person might struggle with alcohol use disorder alongside depression and anxiety. This combination can worsen each condition, which makes treatment more complex and demanding.
When a person with a co-occurring disorder doesn’t receive adequate treatment for both issues, they may turn to drugs or alcohol to manage their symptoms. This self-medication can further complicate their health and recovery.
It is required to get specialized co-occurring disorders treatment that addresses both the mental health and substance abuse issues simultaneously. Without treating all aspects of co-occurring disorders, one problem can undermine progress in the other, which can cause hurdles in recovery.
Symptoms of Co-Occurring Disorders
According to SAMHSA’s 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health, approximately 21.5 million adults in the United States have a co-occurring disorder. Common signs of co-occurring disorders include:
- Sudden behavior changes
- Social isolation
- Using substances in risky situations
- Loss of control over use
- Developing tolerance
- Severe withdrawal symptoms
- Intense cravings
Co-occurring disorders can also show up through physical, behavioral, and psychological symptoms, including:
Behavioral Symptoms:
- Using substances to cope with emotions
- Personality changes
- Withdrawal from social activities
- Aggressive or erratic behavior
Physical Symptoms:
- Sleep problems
- Weight fluctuations
- Extreme fatigue
- Poor hygiene
Cognitive Symptoms:
- Paranoia or panic
- Confusion
- Difficulty focusing
Psychosocial Symptoms:
- Mood swings
- Intense agitation
- Feelings of invincibility or detachment
- Suicidal thoughts
Observing and addressing these symptoms is vital for effective co-occurring disorders treatment.
Causes of Co-Occurring Disorders
Co-occurring disorders can arise from a mix of personal and environmental factors. Here’s a look at some common causes:
1. Family History
Genetics can play a role in both mental health issues and substance abuse. If someone has a family history of these conditions, they might be more at risk themselves.
2. Adverse Experiences
Experiencing trauma, like abuse or neglect, can significantly impact mental health. These early experiences can increase the likelihood of developing both mental health and substance abuse problems later on.
3. Odd Situations
High stress from things like financial problems, relationship issues, or work pressures can contribute to both mental health and substance abuse issues. Stress can trigger or worsen these problems.
4. Social Influence
According to Drinkaware’s report on peer impact, 60% of young adults (18-34) who drink believe social pressure to drink to be fit among their peers. Being around friends or social circles who engage in substance abuse can make someone more likely to start using substances themselves. This can further impact their mental health.
5. Lack of Support
Not having a solid support system can increase the risk of co-occurring disorders. Without support, individuals might turn to substance abuse as a way to cope with their mental health challenges.
Addressing these causes demands a combined co-occurring disorders treatment approach. Treating both mental health and substance abuse issues together to tackle the root causes and bring healthy recovery.
Co-Occurring Disorders Treatment
In the US, over 17.5 million Americans are suffering from a mental health disorder and addiction, and unfortunately, 50% of those seek co-occurring disorders treatment. Experts suggest treating both addiction and mental illness together for those with co-occurring disorders.
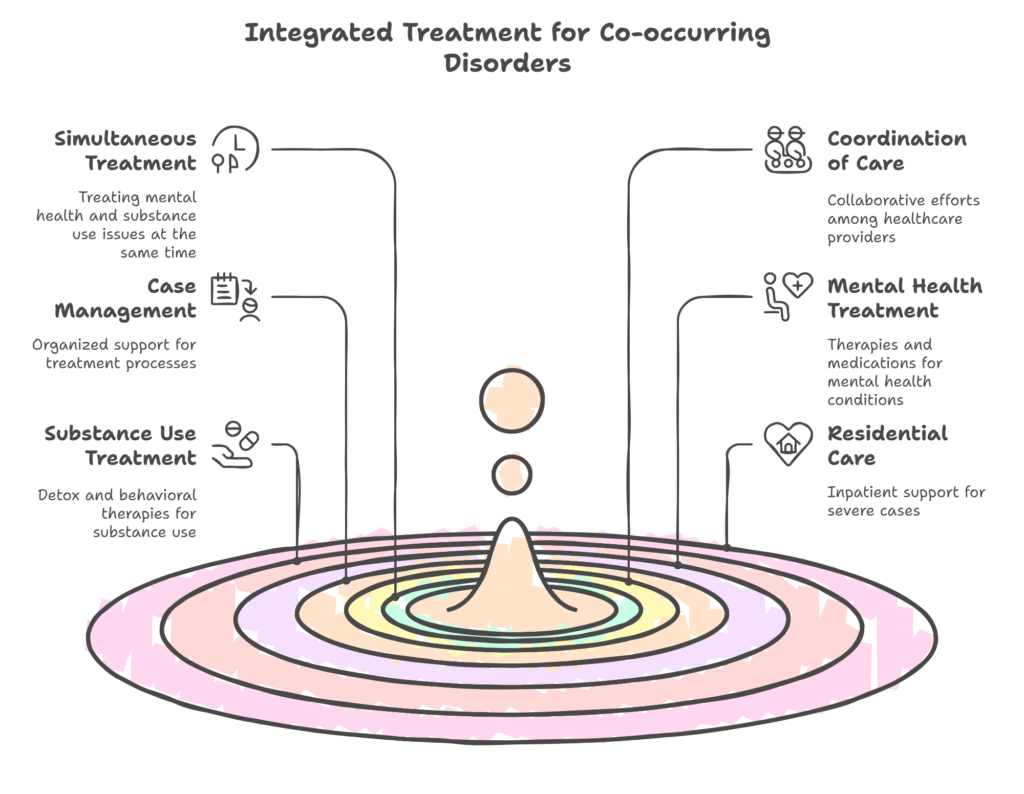
Here are the best-integrated treatments that can be helpful:
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
CBT helps change unhelpful thoughts and behaviors. It’s considered a top treatment for issues like addiction and depression.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
DBT focuses on reducing harmful behaviors, such as self-harm and substance abuse. It’s a good option for people with co-occurring disorders.
Medication
Your doctor might prescribe medicine to help with one or both of your conditions. Some medications can ease symptoms for both issues at once. For example, the FDA-approved bupropion, which can treat depression (Wellbutrin®) and help with quitting smoking (Zyban®).
Support Groups
Support groups are great for getting emotional and social help to stay sober. People in these groups have faced similar challenges. They can share their experiences, answer your questions, and give you advice on handling everyday problems.
Inpatient Programs
Patients live at a facility to detox and address mental health issues.
Outpatient Programs
Patients receive care without staying overnight. Options include Partial Hospitalization Programs (PHPs) and Intensive Outpatient Programs (IOPs).
These co-occurring disorders treatment help develop skills to manage patients’ behaviors and improve their overall well-being.
Your Path to Recovery Begins Here
FAQs: Co-occurring Disorders Treatment
Q: What are the best co-occurring disorders treatment?
A: The best treatment combines behavioral therapies like CBT and DBT, medications, support groups, and sometimes inpatient care for severe cases.
Q: What is dual treatment?
A: Dual treatment, or dual diagnosis, involves addressing both a mental health disorder and a substance use disorder at the same time. This approach ensures that both issues are managed together, which is crucial for adequate recovery.
Q: What is the best way to treat concurrent disorders?
A: For serious cases, specialized care in a hospital or residential setting may be required. Treating both disorders simultaneously is often the most effective approach, requiring a coordinated effort from all involved professionals.
Q: What is sequential treatment for co-occurring disorders?
A: Sequential treatment means addressing one disorder before starting treatment for the other. This approach requires resolving one condition fully before focusing on the second.
Q: What is the recovery stage?
A: Recovery from substance use disorder typically involves three stages: abstinence, which is stopping substance use; repair, which requires healing and rebuilding one’s life; and growth, which focuses on developing new skills and a healthier lifestyle.
How Relevance Recovery Can help?
Overall, co-occurring disorders can be challenging and complex to manage. However, recovery is achievable with the proper support and treatment. If you or a loved one is struggling with substance abuse, it’s crucial to address both the substance use disorder and any accompanying mental health issues simultaneously. Treating just one aspect may not lead to complete improvement, as these conditions often worsen each other.
A good co-occurring disorders treatment and support can pave the way to a healthier and more balanced life.









